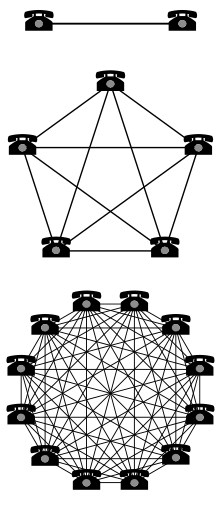
Metcalfe’s Law is a theory related to tecnologia[1] and communications. It suggests that the value of a network is linked to the number of its users. In particular, it argues that the worth of a network is equal to the square of the number of users it has. This concept is often used when looking at social networks and telecommunications. Understanding Metcalfe’s Law is useful for analyzing how networks and social platforms grow and the impact they have. Essentially, the more users a network has, the more valuable it becomes to the community using it. This law was first introduced in 1983 and has been influential in how we understand and value networks.
Lei de Metcalfe states that the financial value or influence of a telecommunications network is proportional to the square of the number of connected users of the system (n2). The law is named after Robert Metcalfe and was first proposed in 1980, albeit not in terms of users, but rather of "compatible communicating devices" (e.g., fax machines, telephones). It later became associated with users on the Ethernet after a September 1993 Forbesarticle by George Gilder.