A web crawler, also referred to as a spider or ant, is a tool that systematically navigates the internet[1] to gather and index information from web pages. Starting from a base list of URLs, known as seeds, it follows links to collect and store content. This data is then archived in a repository for later use. Crucial to the functionality of search engines, web crawlers help in fetching, parsing, and storing web data to keep databases up-to-date. They operate under set policies that guide their selection, revisit, politeness, and parallelization actions. Algorithms and optimization techniques are used to enhance their efficiency, and they also face challenges like handling spam and duplicate content. Their identification is vital for preventing server overloads and for security[2] purposes, as they pose a risk of data breaches when indexing sensitive resources.
A Rastreador da Web, sometimes called a spider ou spiderbot and often shortened to crawler, is an Bot da Internet that systematically browses the World Wide Web and that is typically operated by search engines for the purpose of Web indexing (web spidering).
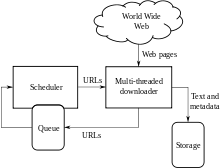
Web search engines and some other sítios Web use Web crawling or spidering software to update their web content or indices of other sites' web content. Web crawlers copy pages for processing by a search engine, which indexes the downloaded pages so that users can search more efficiently.
Crawlers consume resources on visited systems and often visit sites unprompted. Issues of schedule, load, and "politeness" come into play when large collections of pages are accessed. Mechanisms exist for public sites not wishing to be crawled to make this known to the crawling agent. For example, including a robots.txt file can request bots to index only parts of a website, or nothing at all.
The number of Internet pages is extremely large; even the largest crawlers fall short of making a complete index. For this reason, search engines struggled to give relevant search results in the early years of the World Wide Web, before 2000. Today, relevant results are given almost instantly.
Crawlers can validate hyperlinks e HTML code. They can also be used for web scraping e data-driven programming.