Windows 11 is the latest operating system developed by Microsoft[2], officially announced on June 24, 2021, and released on October 5, 2021. This version introduces a redesigned user interface[1] which adheres to the Fluent Design guidelines, incorporating new productivity and social features, security[3] updates, and accessibility enhancements. It also features a refreshed Start menu, a Widgets panel, and tiled sets of windows for improved multitasking. Major additions include support for Android apps, integration of Microsoft Teams, and the replacement of Internet[4] Explorer with Microsoft Edge. It also integrates new gaming technologies like Auto HDR and DirectStorage. To run Windows 11, devices require a minimum of an eighth-generation Intel[5] Core CPU, a second-generation AMD Ryzen CPU, or a Qualcomm Snapdragon 850 ARM system-on-chip, along with UEFI and TPM 2.0 support. As of March 2024, Windows 11 holds a global market share of 26%.
Windows 11 is the latest major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system, released on October 5, 2021. It succeeded Windows 10 (2015) and is available for free for any Windows 10 devices that meet the new Windows 11 system requirements.
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |
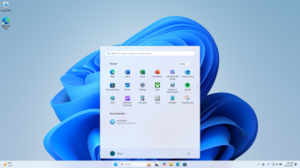 Screenshot showing the new Start menu and centered taskbar, with the Search box | |
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Written in |
|
| OS family | Microsoft Windows |
| Source model |
|
| General availability | October 5, 2021 |
| Latest release | 23H2 (10.0.22631.3447) (April 9, 2024) [±] |
| Latest preview |
23H2 (10.0.22631.3447) (April 9, 2024) [±]
23H2 (10.0.22635.3430) (April 5, 2024) [±]
24H2 (10.0.26100.1) (April 3, 2024) [±]
|
| Marketing target | Personal computing |
| Available in | 88 languages |
List of languages
| |
| Update method | |
| Package manager | .exe, APPX, appxbundle and APK-based (deprecated in March 2024, scheduled for removal in March 2025) |
| Platforms | x86-64, ARMv8.1 |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (Windows NT kernel) |
| Userland | Native API Windows API .NET Framework Universal Windows Platform Windows Subsystem for Android Windows Subsystem for Linux |
| Default user interface | Windows shell (graphical) |
| Preceded by | Windows 10 (2015) |
| Official website | www |
| Support status | |
| See § Versions for more details. | |
Windows 11 features major changes to the Windows shell influenced by the canceled Windows 10X, including a redesigned Start menu, the replacement of its "live tiles" with a separate "Widgets" panel on the taskbar, the ability to create tiled sets of windows that can be minimized and restored from the taskbar as a group, and new gaming technologies inherited from Xbox Series X and Series S such as Auto HDR and DirectStorage on compatible hardware. Internet Explorer (IE) has been replaced by the Chromium-based Microsoft Edge as the default web browser, like its predecessor, Windows 10, and Microsoft Teams is integrated into the Windows shell. Microsoft also announced plans to allow more flexibility in software that can be distributed via the Microsoft Store and to support Android apps on Windows 11 (including a partnership with Amazon to make its app store available for the function).
Citing security considerations, the system requirements for Windows 11 were increased over Windows 10. Microsoft only officially supports the operating system on devices using an eighth-generation Intel Core CPU or newer (with some minor exceptions), a second-generation AMD Ryzen CPU or newer, or a Qualcomm Snapdragon 850 ARM system-on-chip or newer, with UEFI and Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0 supported and enabled (although Microsoft may provide exceptions to the TPM 2.0 requirement for OEMs). While the OS can be installed on devices with unsupported processors, Microsoft does not guarantee the availability of updates. Windows 11 removed support for 32-bit x86 and 32-bit ARM CPUs and devices that use BIOS firmware.
Windows 11 has received a mostly positive reception. Pre-release coverage of the operating system focused on its stricter hardware requirements, with discussions over whether they were legitimately intended to improve the security of Windows or as a ploy to upsell customers to newer devices and over the e-waste associated with the changes. Upon release, it was praised for its improved visual design, window management, and stronger focus on security, but was criticized for various modifications to aspects of its user interface that were seen as worse than its predecessor; some were seen as an attempt to dissuade users from switching to competing applications.
As of March 2024[update], Windows 11, at 26% worldwide, is the second most popular Windows version in use, with its predecessor Windows 10 at 2.5 times the market share. Windows 11 has an estimated 19.75% share of all PCs (the rest being other Windows editions and other operating systems such as macOS and Linux), and an estimated 7.8% share of all devices (including mobile, tablet and console) are running Windows 11.
To comply with the Digital Markets Act, Microsoft is allowing users in the European Union to remove the Edge browser, Bing search engine, and advertisements to comply with users' interests.